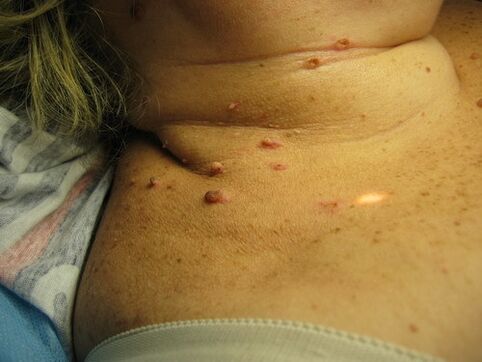
A carrier of HPV may not know they are infected. Symptoms do not appear immediately and only in the form of papillomas of different localization:
- Vulgar. Appear as a small, hard bump about 1 cm in diameter, most commonly on the hands.
- Filiform. Small yellow cone-shaped seals often change and grow.
- Plantar warts. Often confused with calluses.
- Apartment. Itching before the manifestation, similar to the manifestation of an allergy. Then they become rounded, light.
- Sharp warts. They are found in intimate places, on the mucous membrane.
In women with formations on the genitals, accompanying signs may appear:
- Heat;
- itching;
- violation of the cycle;
- pain, blood at the sites of neoplasms.
In men, HPV rarely manifests itself in the form of genital warts, they act as carriers of the disease.
Blood test for papillomavirus type 18 (16)
A blood test for human papillomavirus in developed countries is used for mass detection of carriers and sick people. The diagnostic reliability of cytology can reach 95%. A DNA test in the USA is carried out for the following indications:
- In women over 30, as a screening test;
- Identify questionable search results;
- In the absence of screening programs;
- For monitoring after removal of cervical cancer.
The list of diagnostic procedures for the detection of papillomavirus:
- Cytological examination in combination with the Digene test allows you to determine the clinically significant concentration of the virus in the blood;
- Urological and gynecological examination - to detect genital warts, genital warts;
- Histological examination of a piece of tissue taken after a gynecological or urological examination.
The main task of papillomavirus diagnosis is the detection of precancerous conditions. Colposcopy and cytology are the most common and affordable ways to diagnose the disease.
Transfer Methods
Among the mechanisms under the influence of which you can become infected are:
- Contact;
- vertical (from mother to child during labour).
The implementation of the contact mechanism is carried out through sexual and contact-household. Therefore, HPV can be transmitted by:
- handshake and kiss;
- use of other people's hygiene products, which include razor, washcloth, soap, towel and cosmetics;
- wear clothes belonging to the carrier of the infection;
- visit public baths, saunas and swimming pools.
Oncogenic types of the virus are sexually transmitted. The risk of infection increases many times in people who have promiscuous partners. The more often they change, the higher the risk of infection, and even using a condom you cannot be sure of your safety.
You can also become infected through homosexual relations, since it is they that are characterized by damage to the epithelium and mucous membrane. And a condom in this case does not really help either. The presence of warts on the body of a sexual partner also signals the possibility of contracting HPV through bodily microtraumas.
Pregnant women with HPV should be aware of the possibility of infecting a child when passing through the birth canal.
Infection is carried out only in the presence of characteristic growths in the genital area and cervix. At the same time, papillomavirus infection in a child manifests itself in the form of growths in the larynx, which pose a special danger. It will be difficult for the baby to breathe and eat, possibly even choking.
To begin with, it should be said that the papilloma is transmitted through the epidermis and saliva. At the same time, the infection may not make itself felt for some time and manifest itself in the formation of genital warts and papillomas only with a decrease in immunity. If we talk about how the papillomavirus is transmitted, the likelihood of infection is significantly increased if there are damages, scratches and abrasions on the skin.
Attention! Many people want to know if the papilloma is hereditary. The answer is no. Just when one of the family members is infected, the papilloma virus is transmitted at home or from mother to baby during childbirth.
There is an opinion that the human papilloma virus is most often transmitted through sexual contact. True, but there are also other routes of infection. The incubation period for human papillomavirus can be up to 10 years. Papillomas on the body can be formed by casual contact or by another person's saliva.
There are over a hundred strains of HPV, most of which are transmitted through various types of close contacts.
sexually
HPV is sexually transmitted. This reason is considered the most common and insidious, since often girls and boys are not aware of the presence of infection in the blood. Popular protection methods do not provide 100% security against the virus, especially if it is not a barrier method.
A condom offers a person little protection against HPV. It all depends on the type of infection and the person's immune system.
HPV can affect the skin anywhere on the body. Papilloma is often sexually transmitted.
Infection can even occur through a condom. This is because the virus lives on superficial tissues and readily colonizes mucous membranes.
In the presence of microabrasion, the virus enters the bloodstream and begins its destructive work. As a result of infection, genital warts or cauliflower-like neoplasms appear on the mucous tissues of the genitals.
Often, men infect their partners during intimate relationships. They have stronger immune systems and rarely show visible signs of infection. If there are many sexual relationships with unfamiliar women, they can act as carriers of the virus for some time. HPV can be transmitted from female to male if the sexual partner has a weakened immune system.
A person who is naturally immune to this virus can get warts, have sex with someone who is sick, and stay healthy. There are cases where one partner has tested positive for HPV and the other negative, despite the fact that they have been living together for a long time.
Other routes of infection
The method of infection by domestic means is quite common, as is the possibility of acquiring an infection during sexual intercourse.
The virus can be transmitted by swimming in contaminated water, outdoor or indoor swimming pools. You can see peculiar growths on the body some time after visiting a bath or sauna where an infected person has been.
HPV is transmitted intranatally or transplacentally. For each method, there is a certain risk of infection.
Research suggests that cesarean delivery increases the likelihood of human papillomavirus infection. During natural childbirth or artificial childbirth in women, the risk of infection does not change.
The recurrent course of respiratory papillomatosis is provoked by the presence of several types of pathogens - 68, 59, 56, 52, 51, 45, 39, 35, 33, 31, 18, 16. Differences in oncogenicityserotypes reside in the ability of each type to determine the number of intracellular divisions.
Transmission of HPV through sexual contact
During sexual intercourse, HPV is transmitted as a sexually transmitted infection. After contact of the blood of a carrier or an infected person with the blood of a donor (through erosion, cracks in the genitals), the virion enters the bloodstream. Clinical symptoms are formed depending on the serotype of the virus:
- Common plantar warts are caused by HPV types 63, 1, 4, 2;
- Flat warts - 75, 41, 28, 49. 10, 3;
- Epidermodysplasia verruciformis is seen in patients with papillomatosis due to serotype 11 or 6.
According to scientists, there are many papillomaviruses that have not yet been examined. Humanity has carefully studied oncogenic representatives, which made it possible to create effective protection against cervical cancer in women.
The mechanism of infection with papillomavirus in a domestic way
The human papillomavirus is a highly contagious virus and, according to statistics, 50 to 70% of the population is infected with it. However, the clinical manifestations of the infection are not so frequent, in about 1-2% of cases. A person does not even realize that he is a carrier of HPV until there is a decrease in immunity and an activation of the virus. By knowing the main modes of transmission of HPV, you can protect yourself from unwanted symptoms. So, HPV - how is the disease transmitted? All possible routes of transmission will be discussed below.
Papilloma: how is it transmitted and what is it?
Currently, about 100 different varieties of the virus are known. Among them there are both harmless to humans and dangerous in terms of the development of cancer.
The following facts may be encouraging: the viruses that cause the formation of warts and papillomas belong to subtypes 6 and 11 which have a low carcinogenic risk. Oncogenic subtypes include strains 16 and 18, which cause cell mutations and cervical cancer.
The papilloma virus multiplies exclusively in the cells of the skin and mucous membranes, causing their uncontrolled division. As a result, a person has the following clinical manifestations:
- various warts (common, flat, plantar);
- genital warts;
- papillomatosis of the mouth and larynx;
- papillomas of internal organs.
The role of the virus in the development of cervical cancer in women and penile cancer in men has been proven, so it is important to know how the papillomavirus is transmitted in order to prevent infection.
Human papillomavirus: modes of transmission
It is impossible to detect on its own the presence of a virus in the body if there is no characteristic growth on the skin or mucous membranes. Specialized medical tests will identify a sleep pathology. The absence of symptoms does not guarantee that a person is not dangerous to others.
How is the papillomavirus (HPV) transmitted? Doctors distinguish several ways.
Contact housekeeping
HPV is transmitted through the household. It should be noted that rarely, but this option for getting an infection with the human papillomavirus (PVI), nevertheless, has the right to exist.
You can get infected by shaking hands, using common household items - towels, slippers, wearing someone else's clothes, especially underwear. Often the infection occurs when visiting the swimming pool, fitness center.
The microscopic organism has such a high activity that HPV is transmitted through saliva, a kiss.
The risk of infection increases if the skin has abrasions, scratches, microcracks and various wounds. People with characteristic manifestations of the disease - warts and papillomas are especially contagious.
A fairly common question: will washing your hands regularly reduce the risk of infection? Of course, clean skin is better protected. However, hygiene measures do not protect against HPV infection.
Is the papillomavirus (HPV) sexually transmitted?
A single sexual contact is enough to infect a person. HPV is transmitted through oral, vaginal and anal sex.
Most often, the infection comes from a man, but the reverse situation is also possible, when a reverse HPV infection is recorded - from a woman to a man.
The predisposing factors are:
- early intimacy at a young age;
- frequent change of sexual partners, because do not forget that the papillomavirus is sexually transmitted;
- the presence of genital warts on the genitals.
The papilloma is also sexually transmitted through homosexual relations, during which minor damage to the skin and mucous membranes of the anal region occurs. This significantly increases the risk of infection, especially if one of the partners has external manifestations of the disease - anogenital warts.
Is the human papillomavirus transmitted during safe sex? Unfortunately yes. HPV is transmitted through a condom, because warts invisible to the eye can be located in the inguinal region not protected by the product.
Using a condom greatly reduces the risk of infection, but does not offer a complete guarantee of safety. Despite this, the use of a condom is recommended for all people with multiple sexual partners.
HPV is easily transmitted through oral sex. This increases the risk of developing tonsil cancer, especially if a person has been infected with oncogenic strains.
Papillomavirus: transmission from mother to child (vertical method)
Many pregnant women worry: is HPV passed from mother to child? Unfortunately, such a route of infection exists, and infection can occur both transplacentally (during the prenatal period) and during childbirth.
If the first option is incredibly rare, then when a baby passes through an infected birth canal, a child can get papillomavirus with a high degree of probability.
Possible infection of the larynx, bronchi and trachea in a newborn. The virus is introduced into the mucous membranes and stimulates the formation of growths. Laryngeal papillomatosis can lead to stenosis and suffocation of the child, especially if the vocal cords are affected. Any infection, a cold leads to swelling of the mucous membranes of the respiratory tract, and in the presence of concomitant papillomas, it ends with difficulty in inhaling and exhaling.
Papillomavirus infection (PVI) belongs to the group of anthroponotic pathogens (transmission occurs exclusively from person to person). If we talk about how you can get infected with papillomavirus (HPV), then primarily through sexual contact with an infected partner. In addition, the virus can remain active in dead skin cells for a certain (relatively short) period of time, therefore, in some situations, infection with human papillomavirus is carried out by home means. Now a little more about how to get HPV and what methods of infection exist.
Contagious papillomatosis
First of all, the question should be answered: "Is the papilloma contagious? "Undoubtedly. And the appearance of warts requires complex treatment, including not only the removal of formations, but also the administration of the necessary drugs.
Is latent HPV contagious? Another question frequently asked by patients. The answer will also be positive. It should be known that even the practice of safer sex is not a complete guarantee against infection. The virus can lodge in the groin and the surface of the genitals, unprotected by a condom.
Human papillomavirus: sexually transmitted infection
The main mode of transmission of papilloma is sexual intercourse with an infected partner. This type of transmission is typical of most varieties of viruses with high oncogenic activity.
The risk of contracting the disease is particularly high in men and women who are promiscuous when choosing a sexual partner. People with homosexual inclinations should also be included in the risk group. The practice of anal sex is accompanied by trauma to the skin and mucous membranes, which greatly facilitates the process of introducing HPV DNA into the human body.
A person often considers growths on the skin harmless and treats them with folk methods. This mistake can lead to dangerous consequences - abnormal growth of epithelial tissue exacerbates the spread of papillomavirus throughout the body, and some of its strains cause cell mutation with the formation of various types of cancer.
More than 80% of the world's population carries the human papillomavirus, regardless of age and race.
Human papillomavirus (HPV) is a very common disease against which neither children nor adults are protected. Getting infected with this infection is quite simple, since its cells surround us and retain their viability for a long time without a carrier.
Moreover, it can settle imperceptibly in the human body and will manifest itself only to a certain point. All this time, the infected object is a carrier of the disease, which is why HPV is transmitted both to people who are nearby and to family members.
Papillomavirus - a provocateur of the development of oncology
Almost every third person has small growths on their body that initially seem harmless and harmless. When such neoplasms are discovered, the first reaction of the patient is to tear them out or remove them using folk methods.
In fact, such actions often cause irreparable damage to health, since improper removal of the papilloma can cause active proliferation of epithelial tissues. This is what contributes to the rapid spread of HPV in the body and in some cases even causes skin cells to mutate with subsequent degeneration into a cancerous tumor.
To date, scientists have divided all types of papillomaviruses into three categories:
- sure;
- weakly oncogenic;
- highly oncogenic.
One of the characteristics of HPV is that it is not a sexually transmitted disease in the usual sense. The sexual route is only one route of infection among others, and far from being the main one. This is why condoms cannot always protect against the human papillomavirus.
We propose to determine what methods of transmission of the virus exist, how infection occurs and whether it can be avoided.
In total, about 130 types of human papillomaviruses are known to medicine. Only about 40 of them affect the genitals. For most of these 40 types, the sexual route of transmission is the main one, but studies show that it is not the only one.
HPV prevention
There are a number of preventive measures, thanks to which infection with the human papillomavirus is very likely not to enter the body.
- all damage to the skin should be treated with antiseptics;
- use only personal hygiene products;
- in public saunas, baths and pools it is necessary to use rubber slippers;
- any illness should be treated in a timely manner;
- fidelity to a trustworthy sexual partner;
- use a condom for all sexual intercourse. Although it does not guarantee safety, nevertheless, through a condom, the papillomavirus enters the body of women and men with less probability;
- regular exercise;
- hardening of the body;
- compliance with sleep and nutrition.
Such precautions should be taken not only to avoid HPV infection, but also other sexually transmitted infections. The condom offers a guarantee against infection by many diseases that cause the activation of the HPV virus.
In the event of the presence of a virus in the body of a pregnant woman and its manifestations in the genital area, a full examination and removal of these neoplasms is necessary. If there are papillomas on the genitals, a cesarean section is recommended for a woman to prevent infection of the child when passing through the birth canal.
There is a special vaccine against viruses of highly oncogenic strains, which is recommended mainly for women under 26 and adolescents. Even on the condition that the HPV carrier himself is vaccinated, his immunity improves markedly and the virus goes into an inactive phase.
At the same time, it should be taken into account that the virus does not disappear from the body, and therefore the person remains a carrier of the infection. For safety reasons, he must use a condom during sexual intercourse and only use personal hygiene products.
We have understood how the human papilloma virus is transmitted (women, men and children), now it remains to consider preventive measures. It should be said right away that the most effective way to avoid getting infected is preventive vaccination.
To date, two types of vaccines against this infection are known. They protect against the most dangerous oncogenic strains of viral infection.
However, the high efficiency of such protection is observed only when vaccinated at an early age, before sexual activity or before infection with one of the HPV strains.
In order not to be infected with the human papillomavirus, you must follow some simple rules that will help you avoid other more serious health problems:
- be careful when choosing sexual partners - avoid casual contact;
- follow the rules of personal hygiene - wash your hands more often, especially after visiting public places;
- strengthen immunity - if possible, avoid stress and overwork;
- get vaccinated - the vaccine appeared relatively recently, in 2006.
Even after studying the transmission routes of the human papillomavirus and following all the rules of prevention, it is impossible to completely protect yourself from HPV infection. If you have been in contact with a sick person and you are concerned that the virus could be transmitted, you can take a blood test for PCR. This will give you a reliable answer. But it should be noted that HPV does not require treatment if you do not have characteristic clinical manifestations.















